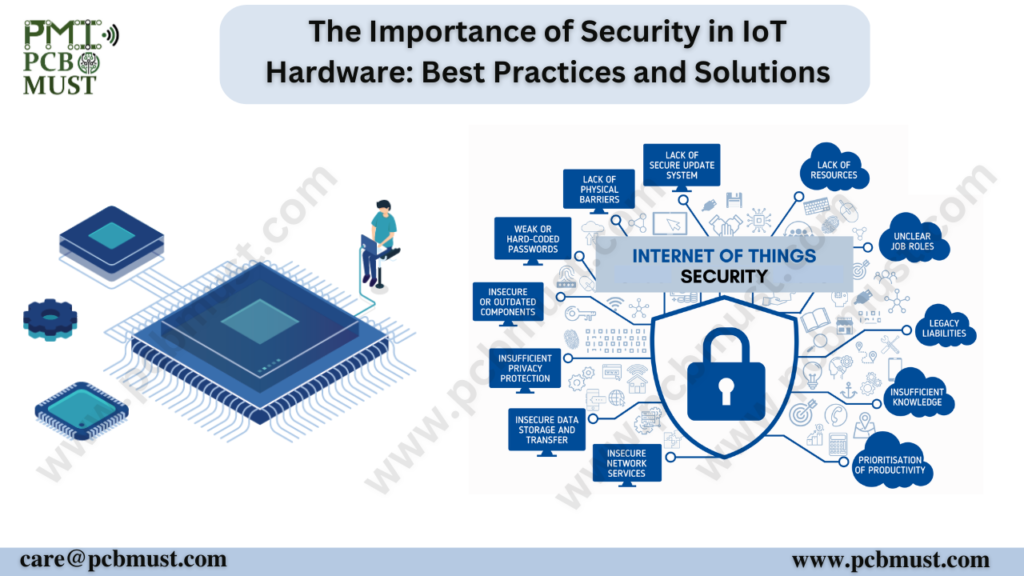
The Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed the way we live and work, with connected devices enabling everything from smart homes to industrial automation. However, with this increased Connectivity & Automation comes the risk of security breaches and data leaks. In this blog, we will explore the importance of security in IoT hardware, and the best practices and solutions for ensuring that IoT devices are protected from cyber threats.IoT refers to the network of interconnected devices and machines that can communicate and exchange data without human intervention. These devices include smart speakers, thermostats, cameras, and other household appliances. They also extend to industrial automation, healthcare devices, and vehicles, among others. The growth of IoT has been phenomenal in recent years, with experts predicting that the number of connected devices will reach 75 billion by 2025.Here are some important facts to consider:
- According to a study by Gemalto, 90% of consumers lack confidence in IoT device security.
- IoT attacks increased by 300% in 2019, according to a report by Nokia..
- A successful IoT attack can have severe consequences, including data breaches, device malfunctions, and even physical harm.
However, IoT devices are vulnerable to cyber threats and attacks, and there are several reasons for this. For one, many IoT devices are manufactured cheaply, with little emphasis on security. Secondly, many IoT devices run on outdated software, making them susceptible to security vulnerabilities. Additionally, the lack of security standards and regulations in the IoT industry poses a significant challenge to cybersecurity.
With these challenges in mind, it’s essential to focus on the security of IoT hardware to ensure that these devices are not exploited by cybercriminals
The Importance of Security in IoT Hardware
The rise of IoT has led to a proliferation of connected devices, ranging from consumer devices like smart speakers to industrial automation systems. However, these devices are often designed with convenience and functionality in mind, rather than security. This leaves them vulnerable to cyber threats, including hacking, data breaches, and malware attacks.
The consequences of a security breach in an IoT device can be significant. In addition to the loss of sensitive data, a compromised device can also be used as a platform for launching further attacks, potentially compromising an entire network. As such, ensuring the security of IoT devices is crucial.
Best Practices for Securing IoT Hardware
There are a number of best practices that can be followed to ensure the security of IoT hardware:
1.Authentication and Access Control:
Devices should require strong passwords and two-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access.
2.Encryption:
Data transmitted between IoT devices and servers should be encrypted to prevent eavesdropping and data theft.
3.Firmware Updates:
Devices should be designed to receive regular firmware updates, which can include security patches and bug fixes.
4.Physical Security:
Devices should be physically secured to prevent tampering or theft.
5.Network Segmentation:
IoT devices should be separated from other devices on the network to prevent attackers from moving laterally across the network.
6.Data Management:
Data should be managed securely, including encryption at rest, and deletion of data when it is no longer needed.
7. Disable Unused Features:
Many IoT devices come with features that users may not need or use. These features can pose a security risk and should be disabled if not needed. Disabling unused features can help reduce the attack surface of IoT devices and prevent potential security threats.
Solutions for Securing IoT Hardware
In addition to best practices, there are a number of solutions available to help secure IoT hardware:
1.Secure Boot:
Secure boot ensures that only trusted code is executed during the device boot process, preventing unauthorized access.
2.Trusted Execution Environments:
Trusted execution environments (TEEs) provide a secure area for executing sensitive code and data, protecting against attacks like code injection.
3.Hardware Security Modules:
Hardware security modules (HSMs) provide a secure area for storing and processing cryptographic keys, protecting against attacks like key theft.
4.Identity and Access Management:
Identity and access management (IAM) solutions can be used to manage access to IoT devices and ensure that only authorized users can access them.
Threat Intelligence: Threat intelligence solutions can provide real-time visibility into threats and vulnerabilities, allowing organizations to respond quickly and effectively to potential security breaches.
5. IoT Security Platforms:
IoT security platforms are designed specifically for securing IoT devices. These platforms provide end-to-end security, from device management to secure communication protocols to encryption. They also include features such as intrusion detection and response, threat intelligence, and compliance management.
Conclusion
The security of IoT hardware is crucial to protecting against cyber threats and ensuring the integrity of data. Best practices like authentication and access control, encryption, and network segmentation, as well as solutions like secure boot and hardware security modules, can help ensure that IoT devices are secure. As the IoT continues to grow, it is essential that security remains a top priority for organizations and manufacturers alike.