Power electronics is a rapidly evolving field that plays a critical role in modern society. However, designing and optimizing power electronics systems can be a complex and challenging task, requiring a deep understanding of electrical engineering principles, advanced mathematical modeling techniques, and a host of other factors. In this blog, we will explore some of the common challenges faced by power electronics designers and seek expert insights on how to solve them.
#powerelectronicsdesign #electronicengineering #expertinsights #electronicsolutions
#circuitdesign
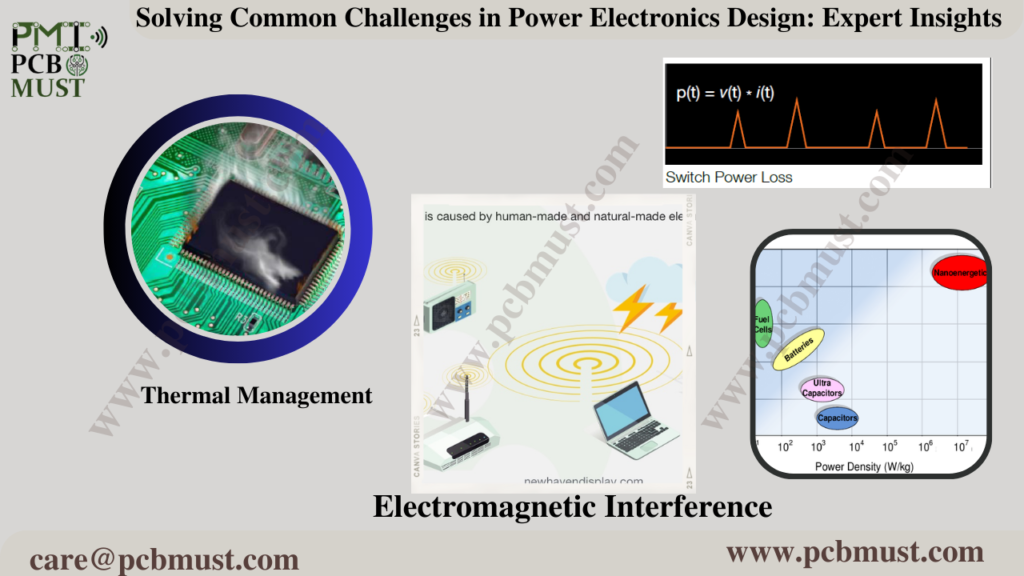
Challenge #1: Switching Losses
Switching losses occur when a power electronics system switches from one state to another. These losses can significantly impact system efficiency and can cause components to overheat and fail prematurely. To mitigate switching losses, designers must carefully select components that can handle the required switching frequency and design circuits that minimize the energy losses associated with switching.
Expert Insight:
According to Dr. John Shen, founder and CEO of Powersim Inc., “The most critical factor for switching losses is the choice of power semiconductor devices. Designers should look for devices with low on-state resistance and low gate charge, as well as those that can handle high switching frequencies.”
Challenge #2: Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
EMI can be a significant problem in power electronics systems, particularly those that operate at high frequencies. EMI can interfere with other electronic devices, causing malfunctions and reducing overall system reliability. To mitigate EMI, designers must use proper grounding techniques and shielding, carefully choose component layouts and filter designs, and minimize the use of high-speed switching.
Expert Insight:
According to Dr. Alex Q. Huang, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at the University of Texas at Austin, “EMI can be mitigated through proper design techniques such as using differential mode filters, common mode filters, and shielding. Additionally, designers can use lower switching frequencies and softer switching topologies to reduce EMI.”
Challenge #3: Thermal Management
Power electronics systems generate a significant amount of heat, and if not properly managed, this heat can cause components to fail prematurely. To manage heat, designers must carefully select components with appropriate thermal properties, design circuits that minimize heat generation, and implement effective cooling strategies.
Expert Insight:
According to Dr. Avinash Kumar, a senior application engineer at Texas Instruments, “Designers should focus on selecting components with low thermal resistance and high thermal conductivity, as well as those with low junction-to-case thermal resistance. Additionally, designers can implement effective cooling strategies such as using heat sinks, fans, and liquid cooling systems.”
Challenge #4: Power Density
Power electronics systems often require high power density, which can be challenging to achieve while maintaining system reliability and efficiency. To achieve high power density, designers must carefully select components with high power densities, optimize circuit layouts and designs, and use advanced packaging techniques.
Expert Insight:
According to Dr. Fred Wang, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at Virginia Tech, “Designers can achieve high power density by using advanced packaging techniques such as direct bonding, wafer-level packaging, and 3D integration. Additionally, designers can optimize circuit layouts and designs to minimize the size of the power electronics system.”
Conclusion
Power electronics design presents a range of challenges, from managing thermal properties to mitigating EMI and achieving high power density. However, with the right techniques and expert insights, designers can overcome these challenges and create highly efficient and reliable power electronics systems. By carefully selecting components, optimizing circuit layouts and designs, and implementing effective cooling and packaging strategies, designers can create power electronics systems that meet the demanding requirements of modern society.